Here, we import some sample Luminex® run data using the new assay design you just created. You will enter batch, run and analyte properties for a single run contained in a Excel single file. (Other topics describe how to
import a multi-file run, how to
import a batch of runs at once, and how to
reimport a run.
Start the Import Process
- If necessary, click the Assay Dashboard tab to return to the folder's main page.
- In the Files web part, open the Luminex folder, and then the Runs - Assay 100 folder.
- Select the file 02-14A22-IgA-Biotin.xls by single-clicking it.
- Click Import Data.
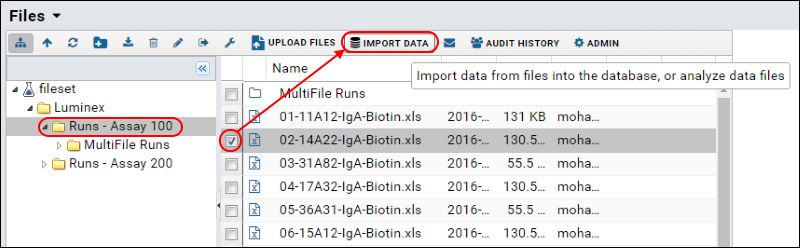
- In the Import Data popup window, select Use Luminex Assay 100 (the design you just created).
- Click Import.
Batch Properties
First, we enter batch properties. These are properties which are set once per batch of runs, which in this first example is only a single run.
- Participant/Visit and Target Study: Leave the default selections ("Sample information in the data file" and "None". These fields are used for aligning assay data with existing participant and specimen data. We will learn more about these fields later in this tutorial.
- Species: Enter "Human".
- Lab ID: Enter "LabKey".
- Analysis software: Enter "BioPlex"
- Click Next.
Run Properties
Next, we can enter properties specific to this run.
- On the page Data Import: Run Properties and Data File, leave all fields unchanged.
- Note that the Run data field points to the Excel file we are about to import: "02-14A22-IgA-Biotin.xls". When you leave the Assay Id field blank (as you do in this step), the name of the imported Excel file will be used as the Assay Id, in this case "02-14A22-IgA-Biotin.xls".
- Click Next.
Analyte Properties
While any assay may have batch or run properties, some properties are particular to the specific type of assay. Analyte properties defined on this page are an example.
Well Roles
If a sample appears at several different dilutions, we infer you have titrated it. During the import process for the run, you can indicate whether you are using the titrated sample as a standard, quality control, or unknown.
A standard is typically the titration used in calculating estimated concentrations for unknowns based on the standard curve. A quality control is typically a titration used to track values like AUC and EC50 over time for quality purposes. Learn more in
Luminex Calculations.
Here, we elect to use
Standard1 (the standard in the imported file) as a
Standard.
In this panel you will also see checkboxes for
Tracked Single Point Controls. Check a box if you would like to generate a Levey-Jennings report to track the performance of a single-point control. Learn more in the Level II tutorial which includes:
Step 5: Track Analyte Quality Over Time and
Track Single-Point Controls in Levey-Jennings Plots.
Analyte Properties
The
Analyte Properties section is used to supply properties that may be specific to each analyte in the run, or shared by all analytes in the run. They are not included in the data file, so need to be entered separately. For example, these properties may help you track the source of the beads used in the experiments, for the purpose of quality control. In the second tutorial we will
track two lots of analytes using these properties.
- On the page Data Import: Analyte Properties leave the sections Define Well Roles and Analyte Properties unchanged.
- Click Save and Finish.
View Results
The data has been imported, and you can view the results.
- In the Luminex Assay 100 Runs table, click 02-14A22-IgA-Biotin.xls to see the imported data for the run.
- The data grid will look something like this:
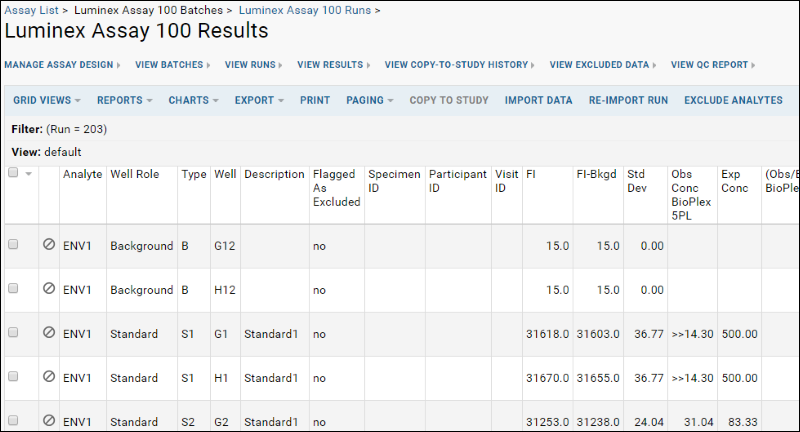
Note that some views of Luminex assay data will have filters already applied. These are listed in the
Filter: panel above the data grid. Hover over the panel to see action buttons including
Clear All if you want to remove these filters.
After excluding some analytes in the next step, you will reimport this run to see that when reimporting, the properties you entered are retained simplifying subsequent imports.
