This topic will help you enable LabKey Server to execute R reports against a remote Rserve instance. Although you could technically run Rserve on the same machine where LabKey is installed, it is not advised. Running R scripts on a remote Rserve server has a number of advantages:
- A remote Rserve server frees up resources on your local machine for other uses and does not overwhelm the machine running your LabKey Server.
- It provides faster overall results, because there is no need to recreate a new R session for each process.
- There is no need to wait for one process to end to begin another, because LabKey Server can handle multiple connections to Rserve at one time.
To follow the steps below, we assume that:
- You are a SysAdmin with a working knowledge of Linux installations.
- You have a working knowledge of R and the basics of how to take advantage of Rserve integration features.
- You are a site administrator on your LabKey Server and will be installing Rserve on another machine.
Topics
Rserve Installation on Linux (Ubuntu)
To install RServe follow the installation steps in the official RServe documentation here:
The process is roughly as follows, though the above may have been updated by the time you are reading this topic:
- Create the Linux server.
- Configure port 6311 to be accessible.
- Install R on your Linux server
- Now, install the Rserve package:
- Access R and use command install.packages("Rserve",,"http://rforge.net")
Configure your Rserve so it runs securely
(Strongly recommended):
- Create the /etc/Rserv.conf file (filename is case-sensitive) with the following info:
remote enable
auth required
encoding utf8
plaintext disable
pwdfile /labkey/rserve/logins
- Create a file called logins under /labkey/rserve and setup the credentials in that file on a single line as shown below. The username and password you provide here will be used to run reports on the Rserve server. You'll enter the values provided here into the LabKey Server scripting configuration below:
Start and Stop Rserve
Follow the instructions in the documentation on the official RServe site:
The following steps are for illustration only and may have changed since this topic was written:
Start Rserve
Start Rserve via the following command:
If you want to start Rserve with the following conditions, an alternative set of parameters can be used. To tell R:
- not to restore any previously saved session
- not to save the environment on exit, and
- to suppress prompts and startup text use the following alternative start command:
R CMD Rserve --no-restore --no-save --slave
Learn more about other command line options in the
Rserve documentation.
To run Rserve in debug mode, use:
R CMD Rserve.dbg --no-restore --no-save --slave
Stop Rserve
To stop Rserve:
Run the
grep command to find the Rserve process:
Identify the PID of the process and use the kill command to terminate the process.
Enable Scripting Using Rserve on LabKey Server
Once Rserve is installed and running as described above, a site administrator must complete these steps to configure LabKey Server to use it. A grid detailing the required settings and properties follows the image.
- Go to > Site > Admin Console.
- Under Configuration, click Views and Scripting.
- If there is already an "R Scripting Engine" configuration, select and delete it.
- Add a New Remote R Engine configuration.
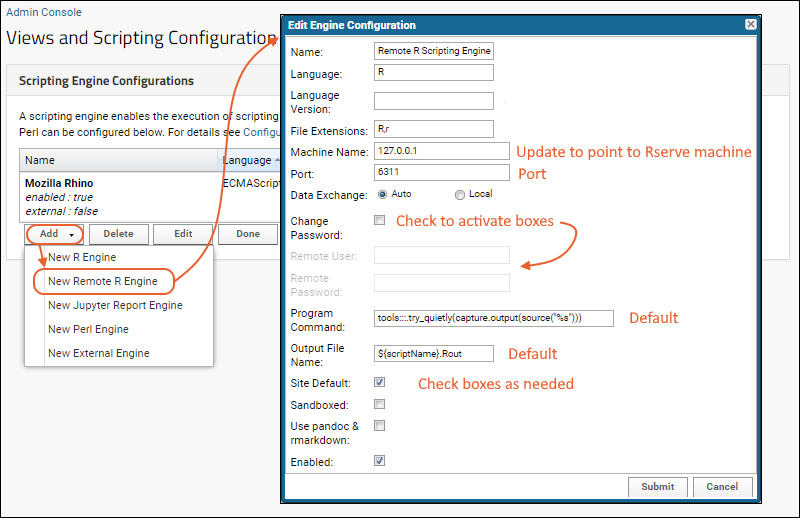
Properties, examples, and descriptions of the configuration options. Items you will need to edit/provide in this panel are in bold.
| Setting | Example value | Description |
|---|
| Name | Remote R Scripting Engine | Default |
| Language | R | Default |
| Language Version | | Manual entry; can be helpful if kept updated. |
| File Extensions | R,r | Default |
| Machine Name | IP Address or DNS name (127.0.0.1 by default) | Machine/DNS name or IP address of running Rserve instance. |
| Port | 6311 | Port that the Rserve instance is listening on |
| Data Exchange | Auto | The default "Auto" setting is typically used. Learn more below. |
| Change Password | Check | Check to activate boxes for entering credentials. |
| Remote User | rserve_usr | Name of the user allowed to connect to an Rserve instance. This user is managed by the admin of the Rserve machine and designated in the "/labkey/rserve/logins" file. |
| Remote Password | rserve_pwd | Password for the Rserve user designated in the "/labkey/rserve/logins" file |
| Program Command | tools:::.try_quietly(capture.output(source("%s"))) | This default is provided. |
| Output File Name | ${scriptName}.Rout | This default is provided. |
| Site Default | Checked | There is typically a single remote R configuration on a server. |
| Sandboxed | Check if this Rserve instance is considered sandboxed | Learn more here. |
| Use pandoc & rmarkdown | Check to use pandoc and rmarkdown | Learn more here. |
| Enabled | Check to enable this configuration | |
Click
Submit to save the configuration, then
Done to exit the scripting configuration page.
Data Exchange Options
Auto:
(Default)The "Auto" configuration is the most common and offers secure and reliable operation. Rserve is running remotely without access to a shared file system. In this case, the report's working directory is copied to the remote machine via the Rserve API before the report script is executed. After the script completes, that working directory is copied "back".
This has the advantage of allowing Rserve in a very generic configuration without direct access to LabKey Server's file system. This can improve security and reduce chances for mistakes.
Note that pipeline jobs and transform scripts can only be run against the "Local" option. An error will be raised if you run them against a remote script engine set to "Auto".
Local:
If Rserve is running on the local machine, that local machine can access the files in the same directory where LabKey Server accesses them. This is not suitable for a large or shared installation, but can be seen as an alternative to using the local "R Scripting Engine" option in certain circumstances.
Running the Rserve as a systemd service can ensure that it stays up and running.
Legacy Options, Developer Guidance, and Troubleshooting
Learn about the legacy "Mapped" data exchange option in the documentation archives
here.
Learn about possible client code changes needed in some situations in the documentation archives
here.
Additional troubleshooting guidance is available in the documentation archives
here.
Related Topics