The
Panorama Chromatogram Libraries Tutorial shows you how to build a chromatogram library for peptides. The same type of functionality is available for small molecules, as shown in the example on this page.
Highlights and attributes for small molecules include ion-mobility types of data like cross-sectional profiles and mobility, collision energy, and more.
Topics
Upload Documents
Obtain your Skyline file. Within Skyline, you will publish to Panorama, or you can use the Data Pipeline to import within Panorama. You can find a few examples in the
LabKey test data on github if you want to demo these tools before you have your own data.
In this walkthrough, we start with the "SmMolLibA.sky.zip" and later import the "SmMolLibB.sky.zip" file to show how to resolve conflicts. While this example shows small molecule data, the features are by no means limited to that type of data.
Follow the steps in the
Panorama Chromatogram Libraries Tutorial to create a place to work.
- Create a new folder of type Panorama, selecting Chromatogram library.
- Click the Data Pipeline tab.
- Click Process and Import Data.
- Drop your Skyline file(s) into the target area to upload them.
- Select the desired file, then click Import Data.
- In the popup, confirm that Import Skyline Results is selected, then click Import.
- You will see import progress in the pipeline. When complete, continue.
All Skyline files uploaded to a library folder will be eligible to include in the .clib file. Whether or not the user has to resolve conflicts, Panorama will choose the molecules based on their Q values, if available. Panorama will choose the one with the minimum Q value as the reference trace. If Q values do not exist, Panorama will then pick the one with the most intense peak. Options for the user to pick which trace to use in the library will not be supported in this iteration.
The Quantitative/non-quantitative flag for transitions shall be added to the .clib file.
See Summary Data
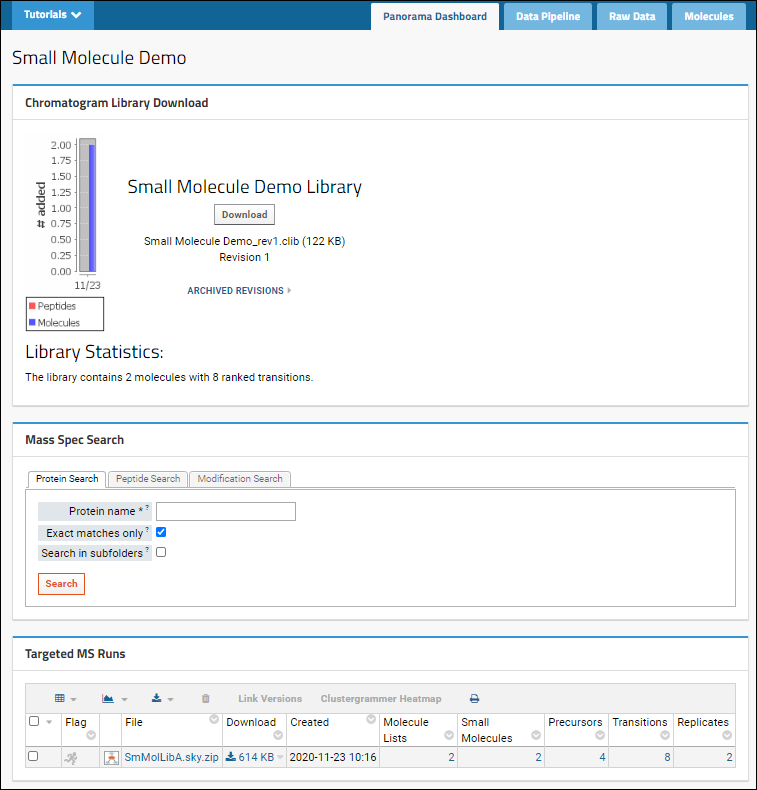
Click the
Panorama Dashboard tab to see the overview of the data available in this library. Note the
Molecules tab on the right, shown when small molecule data is present.
Note that if you checked the box to "Rank peptides within proteins by peak area" you will see a different dashboard combining information about proteins and peptides with your small molecule data. If you see the tabs Peptides and Proteins, you may want to recreate the folder without that box checked to work with small molecule data.
Tour Page Layouts and Folder Tabs
As shown above, there are three web parts:
- Chromatogram Library Download: Summary information, statistics, and a button to download this revision.
- Mass Spec Search: Search for proteins, peptide sequences, or peptides with specific modifications.
- Targeted MS Runs: This panel lists the Skyline files you have imported, with the counts of molecule lists, small molecules, precursors, transitions, and replicates.
Click the
Molecules tab for lists of molecules and precursors.
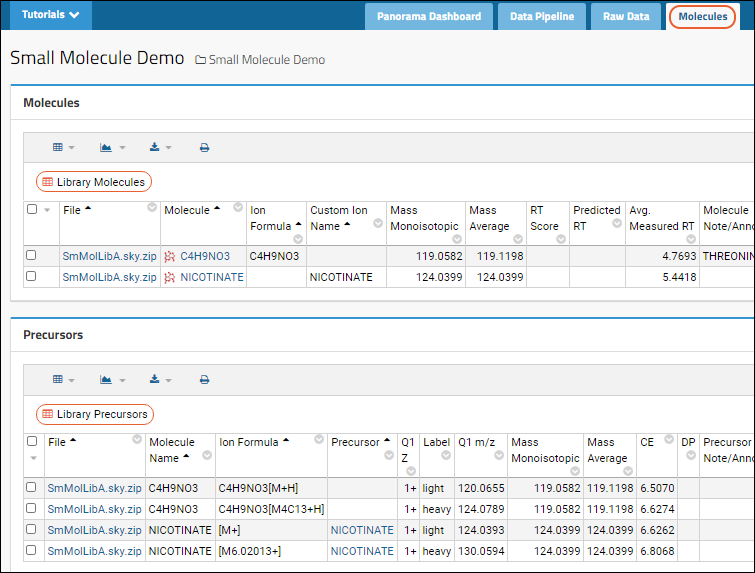
View Details and Chromatograms
Click the name of a molecule in the
Molecules webpart,
Molecule column (shown here "C4H9NO3") for a summary, listing of precursors, chromatograms, and panel for generating summary charts at the bottom of the page.
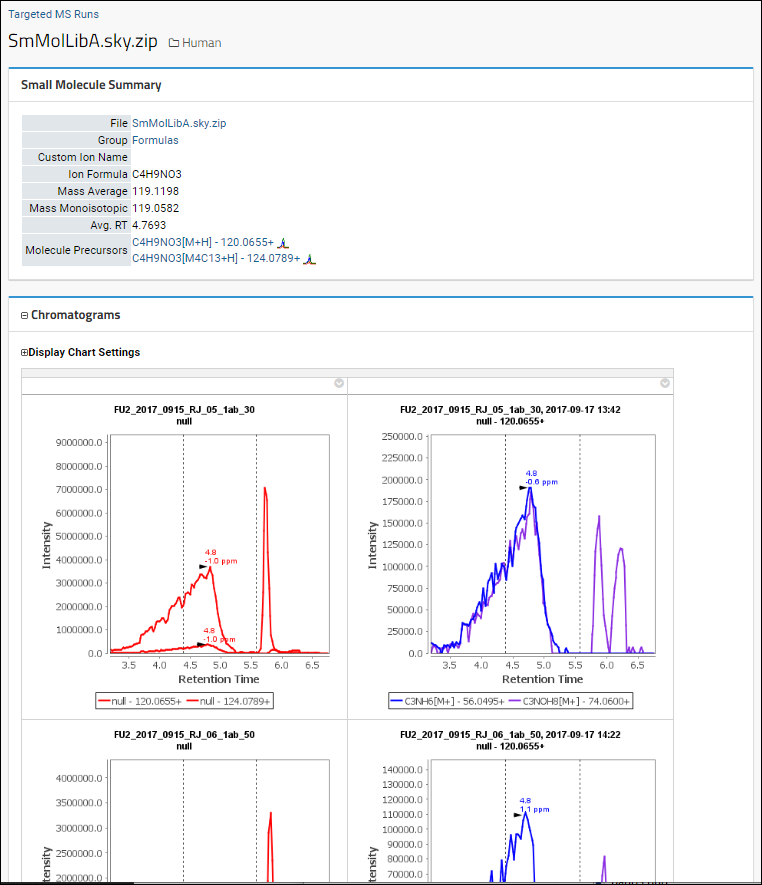
Learn about chromatogram settings and options in this topic:
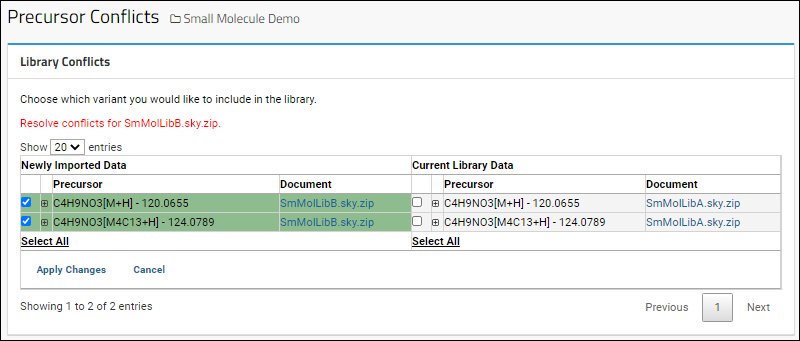
Resolve Conflicts
If documents are imported with conflicting information, the dashboard will show a message indicating the number of conflicting molecules. You must resolve all conflicts before you can extend this library. Click
Resolve Conflicts to do so.
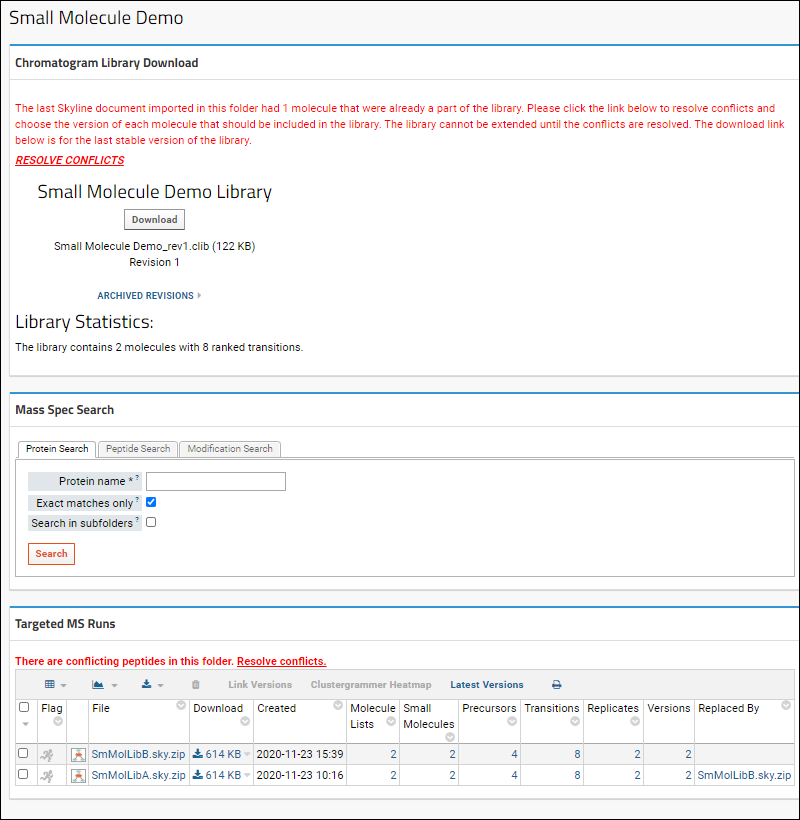
For each conflict, you will see the
Newly Imported Data on the left and the
Current Library Data on the right. In each row, select the checkbox for the version you want to include in the library. Click
Apply Changes when finished.
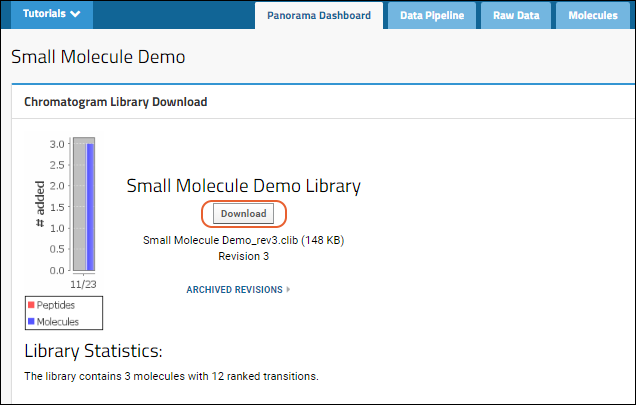
Download .clib SQLite Files
To download the .clib SQLite files, click
Download on the
Panorama Dashboard.
You can import this .clib SQLite file into Skyline and use it to score future experiments.
Note that if you download the library while there are unresolved conflicts, you will download the latest stable version of the library (i.e. it may be missing more recently added information).
Related Topics
 For each conflict, you will see the Newly Imported Data on the left and the Current Library Data on the right. In each row, select the checkbox for the version you want to include in the library. Click Apply Changes when finished.
For each conflict, you will see the Newly Imported Data on the left and the Current Library Data on the right. In each row, select the checkbox for the version you want to include in the library. Click Apply Changes when finished.
 You can import this .clib SQLite file into Skyline and use it to score future experiments.Note that if you download the library while there are unresolved conflicts, you will download the latest stable version of the library (i.e. it may be missing more recently added information).
You can import this .clib SQLite file into Skyline and use it to score future experiments.Note that if you download the library while there are unresolved conflicts, you will download the latest stable version of the library (i.e. it may be missing more recently added information).