Tables and queries can have associated XML files that carry additional
metadata information about the columns in the query. Example uses of query metadata include:
- Column titles and data display formatting
- Add URLs to data in cells or lookups to other tables
- Add custom buttons that navigate to other pages or call JavaScript methods, or disable the standard buttons
- Color coding for values that fall within a numeric range
- Create an alias field, a duplicate of an existing field to which you can apply independent metadata properties
Topics
You can edit or add to this metadata using a variety of options:
Another way to customize query metadata is using an XML file in a module. Learn more in this topic:
Modules: Query Metadata
Edit Metadata Using the User Interface
The metadata editor offers a subset of the features available in the
field editor and works in the same way offering fields with properties, configuration options, and advanced settings.
- Open the schema browser via > Go To Module > Query.
- Select an individual schema and query/table in the browser and click Edit Metadata.
- Edit the fields to adjust labels and other properties.
- Note that there are some settings that cannot be edited via metadata override and are thus inactive in the field editor.
- You also cannot delete fields here, so will not see the icon.
- Expand a field with .
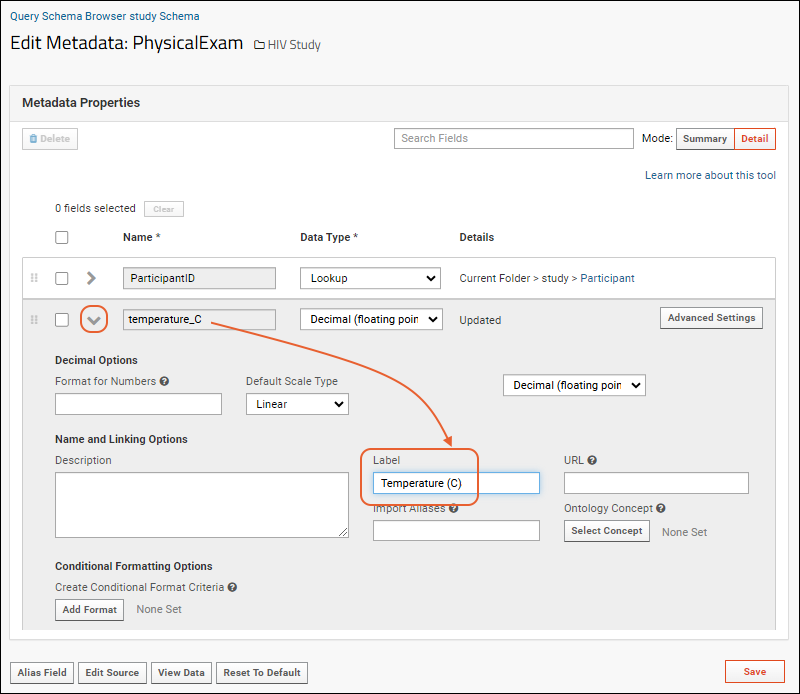
- To change a column's displayed title, edit the Label property.
- In the image above, the displayed text for the column has been changed to include special characters that could cause issues if used in the field name.
- You can directly Edit Source from this interface.
- Click Reset to Default to discard any changes.
- You can also Alias Field and View Data from here.
- Click Save when finished.
Edit Metadata XML Source
The other way to specify and edit query metadata is directly in the source editor.
- Open the schema browser via > Go To Module > Query.
- Select an individual schema and query/table in the browser and click Edit Metadata.
- Click Edit Source to open the source editor.
- The Source tab shows the SQL query; for built in tables, it is read-only.
- Select the XML Metadata tab (if it not already open).
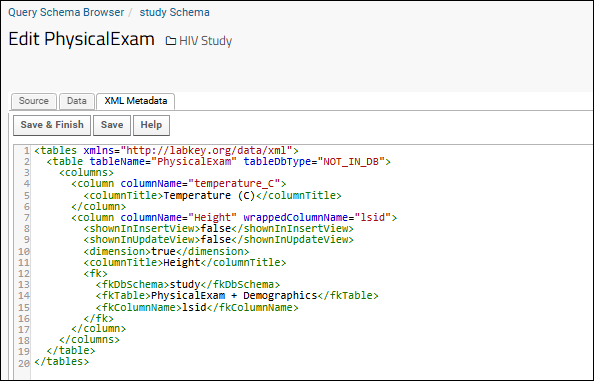
- Edit as desired.
- Click the Data tab to test your syntax and see the results.
- Return to the XML Metadata tab and click Save & Finish when finished.
Examples, including ways to use foreign key (aka lookup) attributes for joining data, can be found here:
Other metadata elements and attributes are listed in the tableInfo.xsd schema available in the
XML Schema Reference.
Note that it is only possible to add/alter references to metadata entities that already exist in your query. For example, you can edit the "columnTitle" (aka the "Label" in the query designer) because this merely changes the string that provides the display name of the field. However, you cannot edit the "columnName" because this entity is the reference to a column in your query. Changing "columnName" breaks that reference.
For additional information about query metadata and the order of operations, see
Modules: Query Metadata.
XML Metadata Filters
The filtering expressions available for use in XML metadata are listed below.
| XML operator | Description |
|---|
| eq | Equals |
| dateeq | Equals for date fields |
| dateneq | Does not equal, for date fields |
| datelt | Less than, for date fields |
| datelte | Less than or equal to, for date fields |
| dategt | Greater than, for date fields |
| dategte | Greater than or equal to, for date fields |
| neq | Does not equal |
| neqornull | Does not equal or is null |
| isblank | Is blank |
| isnonblank | Is not blank |
| gt | Greater than |
| lt | Less than |
| gte | Greater than or equal to |
| lte | Less than or equal to |
| between | Between two provided values |
| notbetween | Not between two provided values |
| contains | Contains a provided substring |
| doesnotcontain | Does not contain a provided substring |
| doesnotstartwith | Does not start with a provided substring |
| startswith | Starts with a provided substring |
| in | Equals one of a list you provide |
| hasmvvalue | Has a missing value |
| nomvvalue | Does not have a missing value |
| inornull | Either equals one of a list you provide or is null |
| notin | Does not equal any of a list you provide |
| notinornull | Does not equal any of a list you provide or is null |
| containsoneof | Contains one of a list of substrings you provide |
| containsnoneof | Does not contain any of the list of substrings you provide |
| memberof | Is a member of a provided user group |
| exp:childof | Is a child of |
| exp:lineageof | Is in the lineage of |
| exp:parentof | Is a parent of |
| concept:subclassof | Ontology module: Is a subclass of a provided concept |
| concept:insubtree | Ontology module: Is in the subtree under a provided concept |
| concept:notinsubtree | Ontology module: Is not in the subtree under a provided concept |
| q | Provide a search string; matches will be returned. |
| where | Evaluating a provided expression returns true. |
| inexpancestorsof | See Lineage SQL Queries. |
| inexpdescendantsof | See Lineage SQL Queries. |
Learn more about filtering expressions generally in this topic:
Filtering Expressions.
Use SQL Annotations to Apply Metadata
You can directly specify some column metadata using
annotations in your SQL statements, instead of having to separately add metadata via XML. These annotations are case-insensitive and can be used with or without a preceding space, i.e. both "ratio@HIDDEN" and "ratio @hidden" would be valid versions of the first example.
@hidden is the same as specifying XML <isHidden>true</isHidden>
SELECT ratio @hidden, log(ratio) as log_ratio
is the same as <displayColumnFactory><className>NOLOOKUP</className></displayColumnFactory>. This will show the actual value stored in this field, instead of displaying the lookup column from the target table.
SELECT modifiedby, modifiedby AS userid @nolookup
: Explicitly set the display title/label of the column
SELECT ModifiedBy @title='Previous Editor'
: Don't compute title based on alias, instead keep the title/label of the selected column.
(Doesn't do anything for expressions.) SELECT ModifiedBy as PreviousEditor @preservetitle
: Apply a numeric format to control the number of decimal places and separator
using a number format string.
SELECT 10/7.0 AS Num @Format='0.00'
Alias Fields
Alias fields are wrapped duplicates of an existing field in a query, to which you can apply independent metadata properties.
You can use alias fields to display the same data in alternative ways, or alternative data, such as mapped values or id numbers. Used in conjunction with lookup fields, an alias field lets you display different columns from a target table.
To create an alias field:
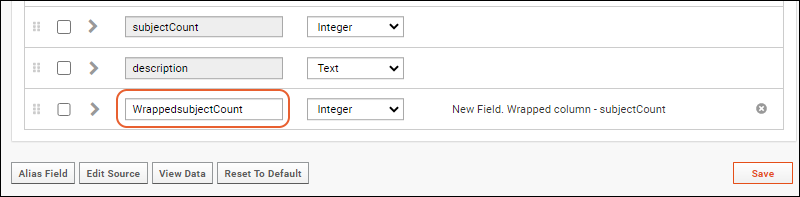
- Click Alias Field on the Edit Metadata page.
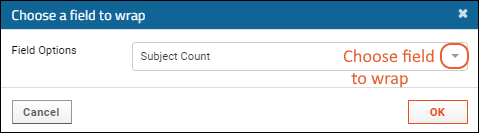
- In the popup dialog box, select a field to wrap and click Ok.
- A wrapped version of the field will be added to the field list.
- You can make changes to relabel or add properties as needed.
- Notice that the details column indicates which column is wrapped by this alias.
You can also apply independent XML metadata to this wrapped field, such as
lookups and joins to other queries.
Troubleshooting
In cases where the XSD for a given type includes a <sequence> element, the order in which you specify elements matters. If you have elements out of order, you may see an error suggesting that you need instead whatever the "next" expected element could be.
Learn more with the example in this topic:
Related Topics


 You can also apply independent XML metadata to this wrapped field, such as lookups and joins to other queries.
You can also apply independent XML metadata to this wrapped field, such as lookups and joins to other queries.